Project Organisation
The figure below summarizes the general organization of this project and the relationships between the workpackages.
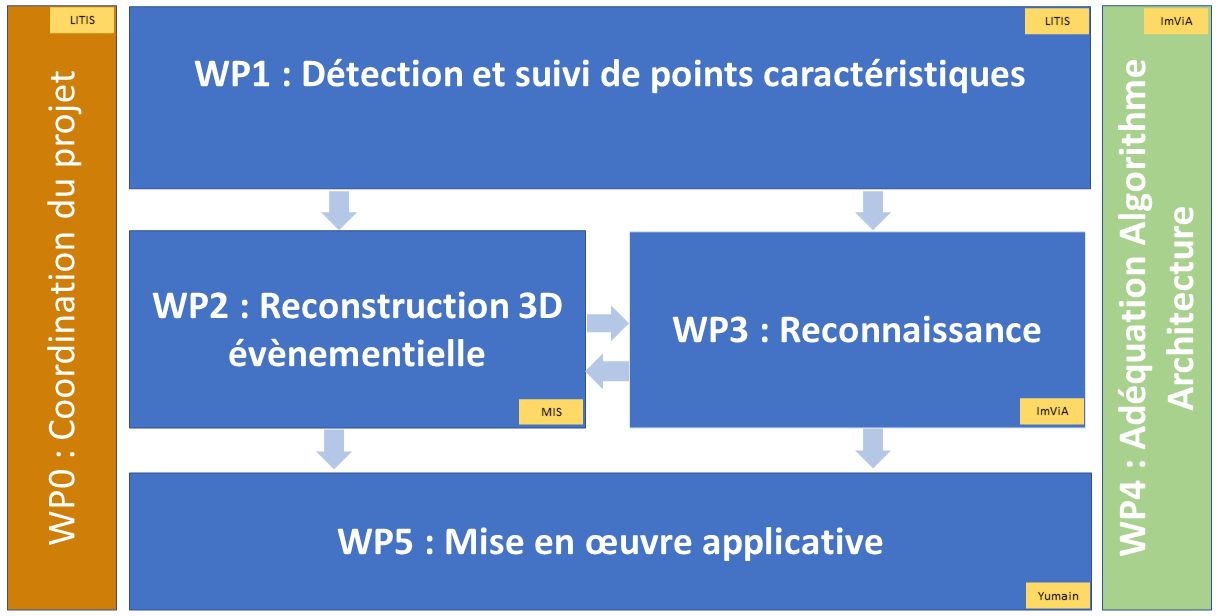
The figure below summarizes the general organization of this project and the relationships between the workpackages.

Responsible Group: LITIS

The purpose of this task is to ensure the technical, financial and administrative organisation of the project. This task will be carried out by LITIS throughout the duration of the project in order to ensure that it runs smoothly according to the planned schedule, that its momentum is maintained and that all partners are involved. Progress reports will be made every 3 months and will give rise to reports. The coordinator will be responsible for the production of the progress reports and the final report. It will also act as an interface with the ANR. Internal and external communication tools (website) will also be updated.

Responsible Group : LITIS
The first objective of this workpackage is to extract characteristic points and their descriptors that are as invariant as possible to motion. This is still a challenge with event vision since the generated events are dependent on the movement of the camera. These characteristic points will feed into the work of WP2 as they will be used to estimate the camera movement and to reconstruct the points in 3D by stereovision, SLAM and using multi-modality with lidar. The proposed descriptors will also be used in WP3 as they can be used for location recognition algorithms. Finally, they will also be used by WP5 to calibrate the system that will be developed. The second objective is to propose methods for estimating the optical flow adapted to our application context, where the majority of state-of-the-art methods impose constraints on the scene or the movement of the camera (uniform optical flow). The estimation of this optical flow will make it possible to segment the moving objects, which will then be reconstructed in 3D (WP2) and recognized (WP3).

Responsible Group : MIS
In this WP, the aim is to produce a three-dimensional representation of the vehicle's surroundings in order to be able to locate it on the one hand and to identify moving objects on the other. The 3D will be obtained either by stereo-event vision or by combining an event camera with a Lidar. In both cases, the scientific challenges will be to combine the data from the two sensors, to estimate the pose, and to detect and track moving objects.

Responsible Group : ImViA
Deep learning techniques based on convolutional networks are now great tools for accomplishing very high-level tasks in computer vision. However, they are not very effective in the case of event cameras since convolutional filters are not necessarily suitable for this type of camera because of the nature of the acquisition. Indeed, convolutional filtering suggests a spatial interdependence between neighboring pixels that is not verified on these images and requires very expensive calculations in computation time while few pixels are activated. This is why this WP aims to revisit deep learning approaches for object and/or place recognition issues while taking advantage of the specificity of these images. WP3 will be strongly linked to the studies carried out in WP1 and WP2.

Responsible Group: ImViA
The ever-increasing complexity of computer vision applications makes it increasingly difficult to achieve algorithmic efficiency at the same time speed of processing. This is all the more crucial in the context of the autonomous vehicle for which reliable and fast 3D perception is required. To do this, In WP4, we propose to adopt a systematic approach of Algorithm Architecture Adequacy based on the Approximate Computing paradigm. The goal is to reduce significantly the complexity of the algorithms while ensuring the best performance, compatible with the application requirements of the autonomous vehicle. The selected solutions will be evaluated on a hardware architecture including a Embedded GPU processor (typically NVIDIA) coupled with various sensors used in the project (1 or 2 event cameras and Lidar). By collaborating actively with the other WPs, WP4 is seen as transversal with the ambition of developing a common scientific methodology applicable to the different algorithms developed in WP1 to WP3 and ultimately to propose technological solutions replicable solutions that can satisfy the real-time constraints of WP5.

Responsible Group : YUMAIN
The objectives of this workpackage are multiple: